- Augusta University
- Colleges & Schools
- Medical College of Georgia
- Physiology
- Faculty | Physiology
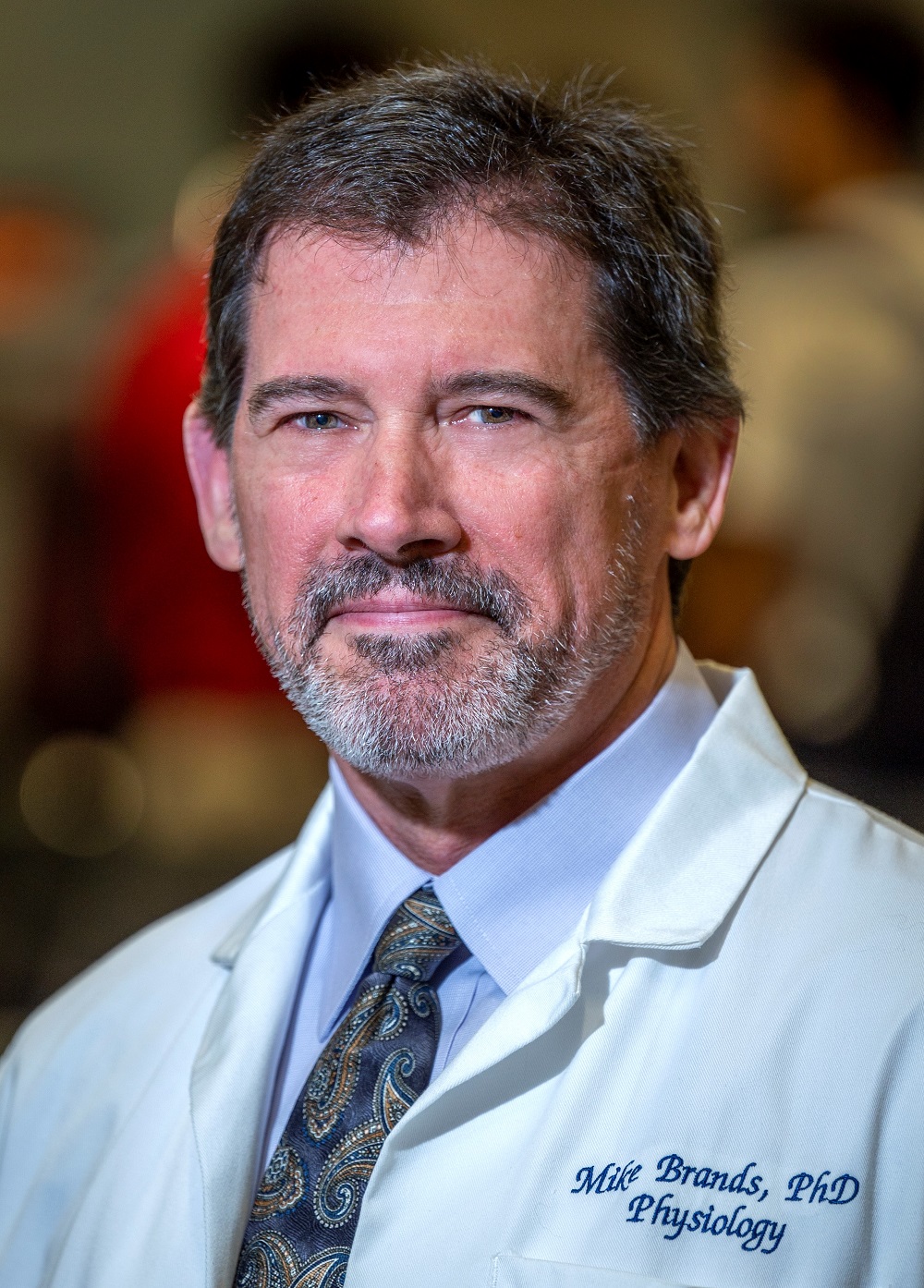
- Michael W. Brands, PhD
Michael W. Brands, PhD
Regents' Professor & Director of Medical Physiology

Phone (706) 721-3529
Fax: (706) 721-7299
E-mail: mbrands@augusta.edu
Office: GB-3330
Lab: CA-3098
Learn more about Dr. Brands' research
Education & Training
Rockhurst Jesuit University,
Kansas City, MO: BS, 1983
Kansas City, MO: BS, 1983
University of Missouri-Columbia,
Columbia, MO: PhD in Physiology, 1988
Columbia, MO: PhD in Physiology, 1988
University of Mississippi Medical Center,
Jackson, MS: Postdoctoral fellowship, 1988-1991
Jackson, MS: Postdoctoral fellowship, 1988-1991
Academic Appointments
Assistant Professor
- 1991
- University of Mississippi Medical Center
Associate Professor
- 1996
- University of Mississippi Medical Center
Professor
- 2000
- Department of Physiology
Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University
Regents' Professor
- 2016
- Department of Physiology
Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University
Research Interests
Cardiovascular-renal integrative physiology and hypertension. Longstanding interest in renal and hormonal mechanisms for chronic blood pressure and circulatory system control in states of insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and diabetes.
Representative Publications
| Brands MW. Unifying Approach for Interpreting the Physiological Effect of High Salt Intake. Hypertension 2020;75:620-622. |
| Klemens CA, Brands MW, Staruschenko A. Postprandial effects on electrolyte homeostasis in the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2019;317:F1405-F1408. |
| Blass G, Klemens CA, Brands MW, Palygin O, Staruschenko A. Postprandial effects on ENaC-mediated sodium absorption. Sci. Rep. 2019;12:4296-4306. |
| Brands MW. The Role of Insulin-Mediated Antinatriuresis in Sodium Homeostasis and Hypertension. Hypertension. 2018 72:1255-1262. |
| Irsik DL, Brands MW. Physiologic Hyperinsulinemia Caused by Acute Hyperglycemia Minimizes Renal Sodium Loss by Direct Action on the Kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018;315:R547-R552. |
| Irsik D, Blazer-Yost B, Staruschenko A, Brands MW. The normal increase in insulin after a meal may be required to prevent postprandial renal sodium and volume losses. Am J Physiol Reg Integ Comp Physiol, 2017 2017;312:R965-R972. |
| Brands MW and Manhiani MM. Sodium retaining effect of insulin in diabetes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 303:R1101-1109, 2012. |
| Manhiani MM, Duggan AD, Wilson H, and Brands MW. Chronic Intra-Renal Insulin Replacement Reverses Diabetes Induced Natriuresis and Diuresis. Hypertension. 2012;59:421-430. |
LAB PERSONNEL
Weston Bush
Research Assistant
Alex Coleman
Research Assistant
 Pictured from left to right: Weston Bush, Alex Coleman (2021)
Pictured from left to right: Weston Bush, Alex Coleman (2021)
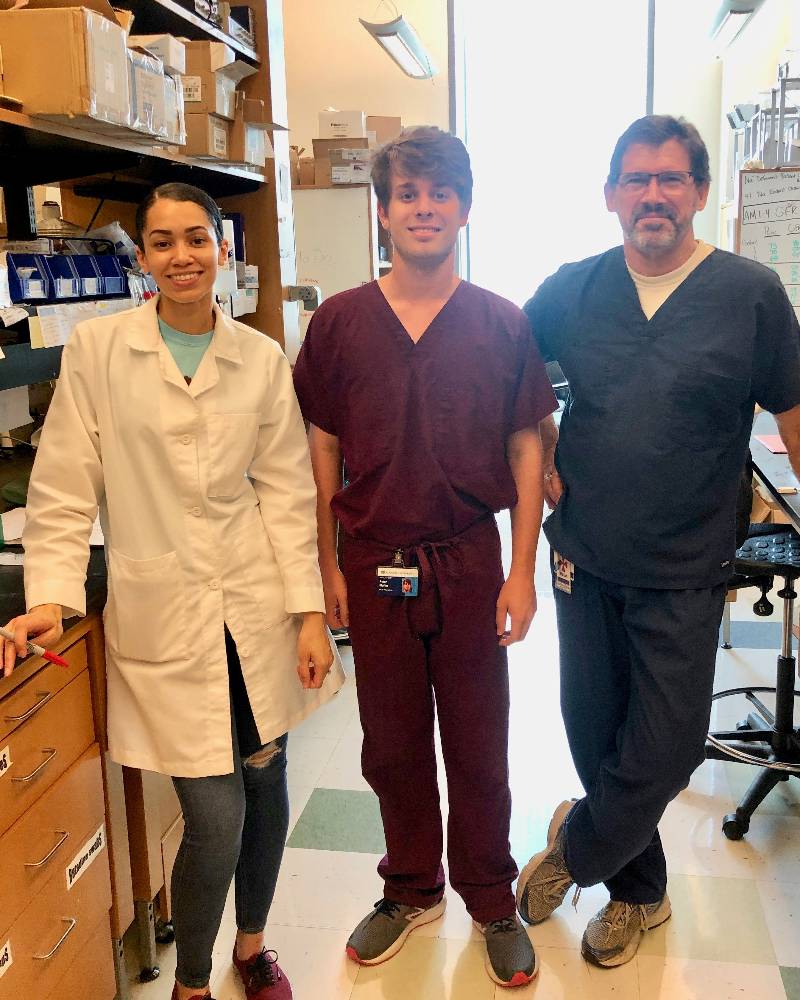 Pictured from left to right: Katherine Hatcher,
Pictured from left to right: Katherine Hatcher,Rob Muller, Dr. Michael Brands (2019)
 Pictured from left to right: Dan Duggan, Rabei Alaisami, Debra Irsik, Michael Brands,
Ashley Washington
Pictured from left to right: Dan Duggan, Rabei Alaisami, Debra Irsik, Michael Brands,
Ashley Washington
